Brain hypoperfusion is a condition in which the brain is not receiving enough blood flow.
This can lead to a variety of problems, including impaired cognitive function, memory loss, and movement disorders.
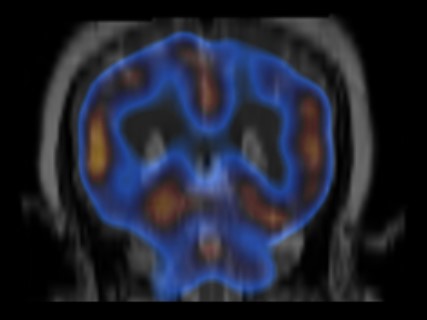
Brain hypoperfusion can be seen on a SPECT brain scan as areas of decreased blood flow.
Brain SPECT Images
The significance of brain hypoperfusion on a SPECT brain scan depends on the clinical context.
For example, brain hypoperfusion in a patient with a history of stroke may indicate that the stroke has caused damage to the brain tissue.
In a patient with dementia, brain hypoperfusion may be a sign of the disease progression.
Some of the clinical conditions associated with brain hypoperfusion include:
Stroke
Dementia
Traumatic brain injury
Multiple sclerosis
Parkinson's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Brain tumors
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Cerebral vasospasm
Hypotension
Anemia
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Drug overdose
There are a number of modalities available to improve brain hypoperfusion. Some of these modalities include :
Medications: There are a number of medications that can be used to improve blood flow to the brain. These medications include vasodilators, which widen the blood vessels, and anticoagulants, which prevent blood clots.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to improve blood flow to the brain. This may involve removing a blood clot or an aneurysm.
Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation therapy can help to improve cognitive function and movement in patients with brain hypoperfusion.
Photobiomodulation therapy (PBMT): PBMT is a treatment that uses low-level light to stimulate the brain. PBMT has been shown to improve blood flow to the brain and to improve cognitive function in patients with brain hypoperfusion.
Infact, we have demonstrated improved perfusion in those brain regions that demonstrated hypoperfusion, using photobiomodulation therapy.
The best treatment for brain hypoperfusion depends on the underlying cause of the condition.
In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about brain hypoperfusion:
Brain hypoperfusion is a serious condition that can lead to permanent damage to the brain.
Early diagnosis and treatment are important for improving the outcome of patients with brain hypoperfusion.
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for brain hypoperfusion. The best treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition and the severity of the symptoms.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of brain hypoperfusion, it is important to see a doctor right away.
What therapies have shows hyperperfusion in known hypoperfusion on spect brain scans ?
There are a few therapies that have shown some promise in improving hypoperfusion on SPECT brain scans. These include:
Photobiomodulation therapy (PBMT): PBMT is a treatment that uses low-level light to stimulate the brain. PBMT has been shown to improve blood flow to the brain and to improve cognitive function in patients with brain hypoperfusion.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS): TMS is a treatment that uses magnetic fields to stimulate the brain. TMS has been shown to improve blood flow to the brain and to improve cognitive function in patients with brain hypoperfusion.
Exercise: Exercise has been shown to improve blood flow to the brain and to improve cognitive function in patients with brain hypoperfusion.
Diet: A healthy diet that is rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids may help to improve blood flow to the brain and to improve cognitive function in patients with brain hypoperfusion.
Ginkgo biloba: Ginkgo biloba is an herbal supplement that has been shown to improve blood flow to the brain.
Bioflex PhotoBioModulation Low Level Laser Therapy
It is important to note that these therapies are not a cure for brain hypoperfusion.
However, they may be able to improve blood flow to the brain and to improve cognitive function in patients with brain hypoperfusion.
More research is needed to determine the best therapies for improving hypoperfusion on SPECT brain scans.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about therapies for brain hypoperfusion:
The best therapy for you will depend on the underlying cause of your hypoperfusion and the severity of your symptoms.
Some therapies may have side effects, so it is important to talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of each therapy.
You may need to try more than one therapy before you find one that works for you.
It is important to continue with therapy even if you do not see results immediately. It may take some time for the therapy to have an effect.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of brain hypoperfusion, it is important to see a doctor right away.
Early diagnosis and treatment are important for improving the outcome of patients with brain hypoperfusion.
Contact us, to discuss further ...



























Comentarios