Introduction
Antioxidant therapy is a type of therapy that uses free radical scavengers (antioxidants) to prevent, delay, or ameliorate many neurologic disorders
Antioxidants work by neutralizing free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the development of various diseases.
In this blog, we will discuss the types of antioxidant therapy, its use in clinical medicine, the mechanism of action, and the concept of super antioxidant therapies, including Ganoderma Lucidem, in neurological disorders.
Types of Antioxidant Therapy
Antioxidant therapy can be classified into three types: endogenous, exogenous, and synthetic. Endogenous antioxidants are produced by the body, such as glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase.
Exogenous antioxidants are obtained from the diet, such as vitamins C and E, carotenoids, and flavonoids. Synthetic antioxidants are artificially created, such as butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT)
Use of Antioxidant Therapy in Clinical Medicine
Antioxidant therapy has been used in clinical medicine to treat various neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Antioxidants have also been used to treat traumatic brain injury and stroke.
Despite promising results in preclinical studies, clinical translation of antioxidants as a therapy to treat neurodegenerative diseases remains elusive
Mechanism of Action
Antioxidants work by neutralizing free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the development of various diseases.
Free radicals are generated by normal cellular metabolism, exposure to environmental toxins, and other factors.
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals by donating an electron, which stabilizes the free radical and prevents it from causing damage to cells
Super Antioxidant Therapies, including Ganoderma Lucidem, in Neurological Disorders
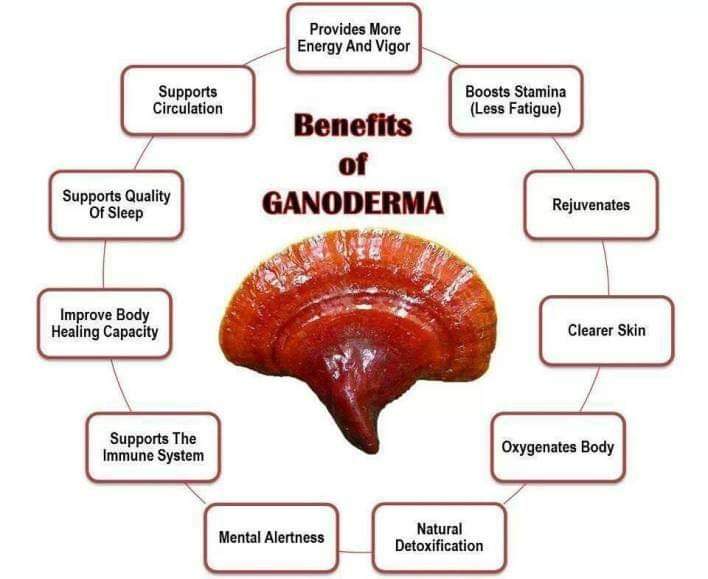
Ganoderma Lucidem is a type of mushroom that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. It is known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and has been studied for its potential use in treating various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis
Ganoderma Lucidem contains polysaccharides, triterpenoids, and other compounds that have been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
Super antioxidant therapies, such as Ganoderma Lucidem, have the potential to provide greater antioxidant protection than traditional antioxidant therapies. However, more research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of these therapies.
What is super-antioxidant therapy and how is it different from regular antioxidant therapy ?
Super-antioxidant therapy is a type of therapy that uses compounds with higher antioxidant activity than traditional antioxidants.
These compounds can scavenge many reactive oxygen species (ROS), induce antioxidant enzymes, and inhibit pro-oxidant pathways. Super-antioxidant therapy is different from regular antioxidant therapy in that it provides greater antioxidant protection than traditional antioxidant therapy.
Regular antioxidant therapy includes natural antioxidant enzymes and vitamins or synthetic agents with antioxidant activity. Super-antioxidant therapy includes compounds such as Ganoderma Lucidem, which has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Other compounds that have been investigated for their super-antioxidant effects include coenzyme Q, melatonin, N-acetylcysteine, resveratrol, and polyunsaturated fatty acids such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA).
Super-antioxidant therapy has the potential to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in neurological disorders, but more research is needed to determine its safety and efficacy.
How do antioxidants work to prevent or delay neurodegenerative disorders ?
Antioxidants work to prevent or delay neurodegenerative disorders by neutralizing free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the development of various diseases.
Antioxidants can scavenge many reactive oxygen species (ROS), including free radicals, peroxynitrites, hydroxyls, peroxyls, and other nitrous oxides.
Antioxidants can also induce antioxidant enzymes and inhibit pro-oxidant pathways1.
Here are some ways antioxidants work to prevent or delay neurodegenerative disorders:
Scavenging: Antioxidants can scavenge free radicals and other ROS, which can prevent them from causing damage to cells.
Termination of lipid peroxidation: Antioxidants can terminate lipid peroxidation, which is a process that can damage cell membranes and contribute to the development of various diseases.
Metal chelation: Antioxidants can chelate metals, such as iron and copper, which can contribute to the production of ROS.
Inducing antioxidant enzymes: Antioxidants can induce the production of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, which can help to neutralize ROS.
Inhibiting pro-oxidant pathways: Antioxidants can inhibit pro-oxidant pathways, such as the activation of NADPH oxidase and the production of nitric oxide synthase, which can contribute to the production of ROS.
Clinical trials or studies on the safety and efficacy of super-antioxidant therapy
There are several clinical trials and studies on the safety and efficacy of super-antioxidant therapy in neurological disorders.
Here are some relevant references:
A review article on clinical trials of antioxidants as cancer prevention agents1.
A review article on prospects for the use of antioxidant therapies in human diseases2.
A clinical trial on the use of antioxidant therapy in patients with septic shock3.
A review article on antioxidant therapeutic strategies in neurodegenerative diseases4.
An article on antioxidant therapy in neurologic disease5.
An article on the significance of antioxidants in the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases6.
These studies suggest that super-antioxidant therapy has the potential to prevent, delay, or ameliorate many neurologic disorders.
However, more research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of super-antioxidant therapy in different types of neurological disorders and to establish the optimal dosage and duration of treatment.
The Organo brand of super-antioxidant therapy

Organo is a brand that offers organic green tea, coffee, and suplements with ganoderma, which is naturally rich in antioxidants. The green tea is made from unfermented leaves and reportedly contains the highest amount of polyphenols antioxidants.
Ganoderma lucidum, also known as the reishi mushroom, is a type of mushroom that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries and is known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties
Organo green tea with ganoderma is a mild-tasting, yet power-packed green tea that is combined with organic ganoderma lucidum for a double dose of flavor
The brand also offers other products, such as red tea, that are rich in antioxidants and amino acids and are designed to support the immune system and promote stress relief.
Here is a listing of the Organo products we have available, at the Durban Neuro Laser Clinic.
What are the effects of combining photobiomodulation therapy with super-antioxidant therapy, in neurological disorders?
There is limited research on the effects of combining photobiomodulation therapy with super-antioxidant therapy in neurological disorders.
However, some studies have shown that photobiomodulation therapy (PBM) can reduce inflammation, oxidative stress, and improve functional recovery in neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis and stroke.
Additionally, super-antioxidant therapy has been shown to reduce oxidative stress and enhance endogenous antioxidant catalase in wound healing.
Therefore, it is possible that combining PBM with super-antioxidant therapy may have a synergistic effect in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in neurological disorders. However, more research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of this combination therapy in neurological disorders
These are the reasons why we choose safe strategic therapeutic synergistic therapies, tailor made for each individual patient.
Conclusion
Antioxidant therapy is a type of therapy that uses free radical scavengers (antioxidants) to prevent, delay, or ameliorate many neurologic disorders.
Antioxidants work by neutralizing free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the development of various diseases.
Antioxidant therapy can be classified into three types: endogenous, exogenous, and synthetic.
Antioxidant therapy has been used in clinical medicine to treat various neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Super antioxidant therapies, such as Ganoderma Lucidem, have the potential to provide greater antioxidant protection than traditional antioxidant therapies.
However, more research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of these therapies.
References
Antioxidant therapy in neurologic disease - PubMed Antioxidant Therapy in Oxidative Stress-Induced Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Clinical Translation - MDPI
Therapeutic Effects of Photobiomodulation Therapy on Multiple Sclerosis by Regulating the Inflammatory Process and Controlling Immune Cell Activity: A Novel Promising Treatment Target Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation[PDF] Photobiomodulation with Super-Pulsed Laser Shows Efficacy for Stroke and Aphasia: Case Studies - Scientific Research Publishing












































































Comments